Foreign companies that want to start doing business in Italy in 2024 may register under one of the legal entities that are available under the Italian legislation or they may operate through a branch or a subsidiary. There are important differences between the two types of companies that should be known by the businessmen and our team of lawyers in Italy can provide in-depth legal assistance on the main characteristics of these two entities.
Table of Contents
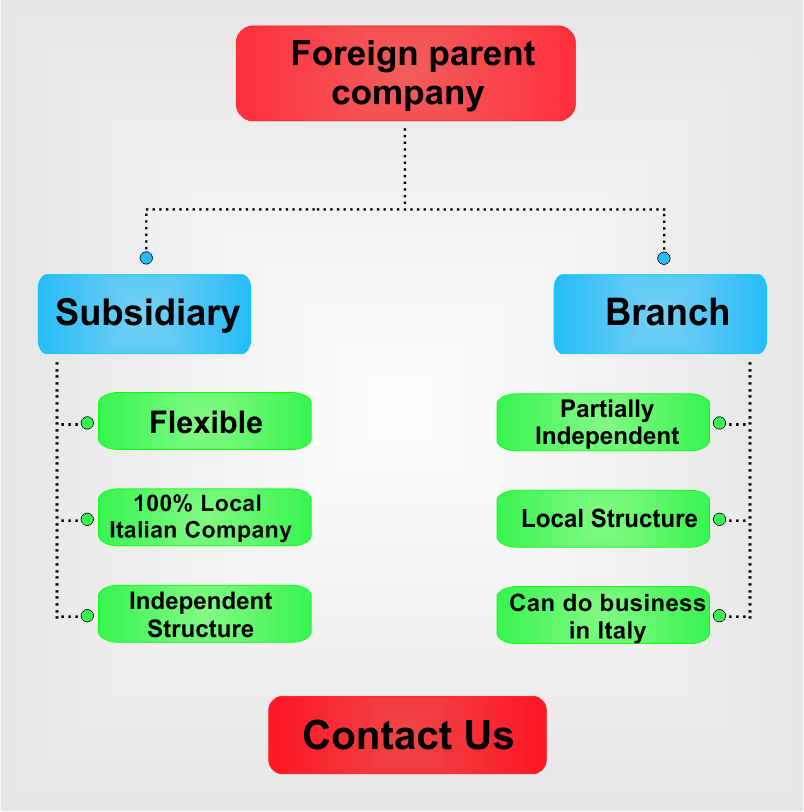
What are the main characteristics of Italian branches/subsidiaries?
When opening a company in Italy that will operate through a branch, it is important to know that the parent company will decide on behalf of the branch, as this business form is dependent on the foreign company and has limited powers. In the case of a company registered as a subsidiary, its representatives will be allowed to make management decisions without the consent of the parent company, as the business form is considered an independent legal entity.
If the investors choose to open a subsidiary, this legal entity can be set up under several business forms prescribed by Italian legislation. An Italian subsidiary can be registered as a public limited company, a private limited company, or a partnership and our team of Italian lawyers can offer more details on the advantages of each structure.
Branches in Italy are seen as dependent structures from the parent company and must be registered for taxation in this country. Each branch must maintain its books, and submit VAT and income tax returns, as the legislation requires in this sense. You can be guided by our Italian lawyers in tax matters for branches in Italy.
More details on the registration of a branch office or a subsidiary in Italy are available in the presentation below:
How to register a branch in Italy
Companies operating in Italy must register with the Italian authorities a set of legal documents. In the case of a branch office, the investors will need to provide information on the parent company, as well as various documents attesting to the incorporation of the branch, as follows:
- the registration certificate of the parent company that wants to set up an Italian branch office;
- the certificate of incorporation and the company’s articles of association and memorandum;
- the names of the company’s secretary and appointed directors (a minimum of one director is required);
- the proof of having a registered office through which the branch will perform its commercial activities in Italy.
If you would like to buy a house in Italy, our suggestion is to collaborate with our lawyers. Having the necessary experience on board, our specialists can check the documentation of the chosen property and the sale-purchase contract, where information about the property, history, buyer and seller, price, and payment method must be mentioned. Contact us today if you want legal support for a real estate transaction.
Public vs. private limited liability company in Italy
The liability of the shareholders of a private limited liability company is limited to their contribution to the share capital, which is why this is the most popular business form registered by both local and foreign businessmen operating in Italy. The company is managed by a board of managers appointed by the general meeting of the shareholders.
In the case of a public limited liability company, the shares can be sold and the entity can be registered with the Stock Exchange. The company can be managed by a person who is a professional and it is not mandatory to be a member of the company.
A great business advantage for subsidiaries in Italy is that such structures can have more than just one activity, under a different name from the parent company. However, regarding the name under which a subsidiary is carrying out its activities in Italy, such a decision must be agreed upon and signed by the parent company.
Other relevant matters on Italian subsidiaries and branch offices in 2024
Registering a subsidiary in Italy does not represent a difficult process and it can be accomplished in one week, if the applicants provide all the necessary documents. For the incorporation of a branch or a subsidiary, it is necessary to address it to a public notary, who will notarize all the documents required by Italian law.
- In the case the foreign company does not control an Italian subsidiary, the ownership share might vary from 1% to 49%. Nonetheless, the foreign company continues to control the votes in further company decisions and changes.
- Both branch offices and subsidiaries are liable for taxation in Italy, but the manner in which taxes are applied will slightly vary. For instance, the branch office is liable for taxation only for the activities carried out in Italy, the parent company is not held accountable for its entire taxable income.
- One of the taxes these entities have to pay is the corporate tax, which, in 2024, is charged at the standard rate of 24%.
For more details related to the similarities and differences between a branch and a subsidiary, foreign businessmen may contact our law firm in Italy. Our Italian lawyers will offer advice and consultancy services regarding the registration procedure in 2024 applicable to these business entities and may advise on the tax regulations available for each structure.

